How the SNMP agent and peers manage the MIBs
While SNMP is the protocol used to communicate network management
information between nodes on a network running on the IP
protocol, the information gathered from each node must
also be in a standard format, so that:
-
the network manager knows what pieces of information can be retrieved
-
the information conveyed via SNMP is understandable to the
software making the request
This standard format is provided by the Management Information Base
(MIB) standard specification. On UnixWare, there are MIB
files for various operating system and hardware parameters.
The MIB files are managed by the SNMP agent
and associated peer processes. A conceptual diagram of how SNMP
works is shown in
``How SNMP works''.
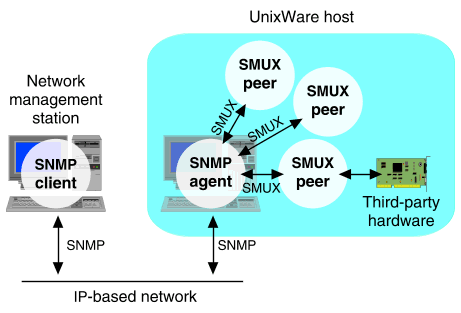
How SNMP works
The SNMP agent's primary function is to listen for SNMP
requests over the network or from another process on the UnixWare machine.
It runs as a daemon process, in.snmpd. The agent manages a subset
of all the statistics in the MIB database.
SNMP peer processes manage the bulk of the MIB
files, and wait for requests from the SNMP agent. The SNMP
agent uses the SNMP protocol to communicate with workstations over
the network. Another protocol, the SNMP Multiplexing Protocol
(SMUX), is used for communication between the SNMP
agent and peer processes. For this reason, SNMP peer processes are
referred to as SMUX peers.
In
``How SNMP works'',
the SMUX peer delivered with UnixWare SNMP
(hostmibd) is shown along with another
custom SNMP peer process that manages a third-party piece of
hardware installed in the UnixWare system. If this program (supplied by
the manufacturer of the third-party hardware) is instrumented for
SNMP, and is configured properly in the SNMP
administrative files, it will respond to SNMP agent SMUX
requests for information from its own private MIB files.
(For information on writing a custom SNMP peer process, see
``Developing SMUX peers for SNMP agents''.)
If the SNMP agent receives a request for MIB data
maintained by one of the peer processes, it communicates the request to the
appropriate peer process using the SMUX protocol. The peer process
then performs the appropriate operation and communicates the result to the
SNMP agent (again via SMUX). Once it receives a reply,
the SNMP agent can then send a reply to the node or process making
the original request. SNMP requests received for information from
a MIB file maintained by the SNMP agent are answered
directly by the agent.
Tasks performed by the SNMP agent
The SNMP agent (/usr/sbin/in.snmpd) does
the following:
-
listens for SNMP requests over the network or from a process on
the same computer (requests arrive in SNMP standard format and
the agent replies with SNMP format packets to the network
management station making the request); IP is the only
supported network protocol
-
registers SNMP peer processes
-
manages a subset of the information in the MIB database (listed in
``RFC 1213 (MIB-II) MIB''
and defined in the file /etc/netmgt/snmpd.defs
-
communicates requests to get or set MIB information that it does
not manage to the appropriate registered peer process (via SMUX)
Tasks performed by an SNMP peer
Two SNMP peer processes are installed with the netmgt
package:
hostmibd-
This daemon runs automatically whenever SNMP is started using the
snmp(1Msnmp)
command, or when the system is rebooted. It manages the MIB
objects listed in
``RFC 1514 Host resources MIB''
and defined in the file /etc/netmgt/unixwared.defs.
NMUSNMP_NWSrvrProtSDiagMIB
NMUSNMP_NWIPXProtSMIB
NMUSNMP_NWProtSSPXMIB
NMUSNMP_NWProtSRIPSAPMIB
Each SNMP peer process:
-
constantly collects operational statistics for the hardware or software
with which it is associated
-
manages the MIB files associated with the statistics it collects
-
waits for requests from the SNMP agent (via SMUX) to
get or set MIB information that it manages
-
performs tasks required to implement a set operation (such as setting the
system date and time)
-
communicates (via SMUX) results of get or set operations requested
by the SNMP agent
All UnixWare peer processes are registered with the SNMP agent
through the snmpd.peers file; see
snmpd.peers(4snmp).
© 2004 The SCO Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
UnixWare 7 Release 7.1.4 - 22 April 2004

