|
|
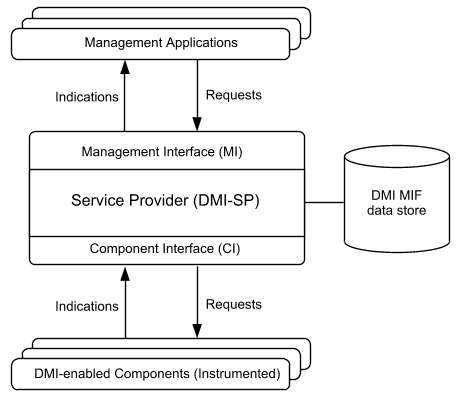
The DMI-SP is responsible for maintaining and delivering management information that describes all DMI-enabled components within its own local node. The general DMI data model represents a store of MIF data that describes managed components.
DMI-enabled management applications register with the MI of the DMI-SP to gain access to MIF data. The MI provides entry points to registered management applications for installing and removing component MIFs, accessing MIF data values and modifying the structure of installed component MIFs.
The DMI Service Provider (DMI-SP) is illustrated in ``DMI 2.0 functional diagram''.

DMI 2.0 functional diagram
The DMI-SP handles Get, Set, List, Add, Delete and implementation-specific functions that are called by management applications. The Service Provider retrieves requested information from the ``component MIF data store'' or ``MIF database''; it performs maintenance on the MIF database and responds to the data requests made by management applications. The DMI-SP also handles indications from components and passes these notifications on to the management applications.
Unsolicited messages sent between DMI entities through the ``Component Interface'' are called either events or indications. The terms are closely related and are sometimes used interchangeably. In this guide, the term ``event'' describes the runtime condition being responded to by a component. The term ``indication'' refers to the notification message sent by an ``event generator'' to alert the DMI-SP that the event occurred. The Service Provider then passes the ``indication'' to any DMI service users.
DMI 2.0 defines an ``Event Model'' that filters and categorizes system indications, providing the management application with a higher level of intelligence about the change in a component's operating status. The Event Model allows indications from various system components to be sent to a management application to alert the user that there has been a change or that there is a problem with the component.