G2++ Programming Language Interface
The most noticeable difference between G2 and G2++ is the radically different
appearance of the G2++ programming language interface.
To illustrate the interface,
we will build the G2++ equivalent to the client program
developed in the last section,
``Adding Builtin C Types to the Repertoire of G2++ Types''.
We start
by compiling the identical usr.g file,
but this time
we use the G2++ compiler
g2++comp(1C++):
$ g2++comp usr.g
to which
g2++comp(1C++)
responds:
usr.g:
=>usr.[hc]
indicating, once again, that two files have been created: usr.h
and usr.c.
The fact that we compiled the identical usr.g
file illustrates
an important point: the G2++ record definition language is a strict
superset of the G2 language; we will look at G2++ language extensions
later in this paper, but for now, suffice it to say that the
common subset has identical semantics in both languages.
This means that
a G2++ program and a G2 program that use the same
record definition
cannot be told apart by purely external means.
The usr.h produced by
g2++comp(1C++)
contains a somewhat different- looking structure
definition for type USR:
usr.h -- generated by g2++comp(1C++)
#include <String.h>
#include <Vblock.h>
typedef struct USR{
String login;
struct{
long usr;
short grp;
}id;
String name;
Vblock<long> proj;
USR();
}USR;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const USR& x);
istream& operator>>(istream& is, USR& x);
Next, we write the client C++ program:
main.c - C++ program
#include <g2++.h>
#include "usr.h"
main(){
String name;
while( name=g2seek(cin) ){
if( name == "usr" ){
USR u;
cin >> u;
u.id.grp += 100;
cout << u;
}else{
G2BUF b;
cin >> b;
cout << b;
}
}
}
Finally, we compile and link this program together with the .c
file produced by the G2++ compiler,
plus I/O routines
from the library:
$ CC main.c usr.c -l++
Perhaps the most surprising thing about the C++ version
of main.c is that it appears
to use only three I/O routines (as compared with five for the C program):
g2seek(cin); Find the next record and return its name
cin >> x; Extract a record from cin into x
cout << x; Insert a record from x into cout
where x may be either of type G2BUF or type
USR.
The right shift and left shift operators, called
extractors and
inserters, respectively, are actually overloaded:
Untyped inserters and extractors-
If x is
of type
G2BUF (a type
defined in the header file
g2++.h), then
this is an untyped
inserter or extractor.
A G2++ application uses the untyped operators when it lacks
a priori knowledge of the types of records it manipulates.
A good example of such an application is the G2++ compiler,
g2++comp(1C++).
A
G2BUF is a navigable syntax tree
whose
hierarchical structure
is isomorphic to that of the G2++ record from which it is constructed.
Your program
can ``navigate'' a G2BUF
by following root,
child, and
next pointers, exactly as you would do in a G2 program.
Untyped inserters and extractors do the work of the G2
functions putbuf(),
getbuf(), and getbuf1() (functions that constitute
what Weythman calls G2's ``interpreted interface'').
The untyped inserters and
extractors are declared in g2++.h; their behavior
is specified in
untyped_io(3C++).
Typed inserters and extractors-
If x is of
type
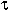 , where
, where 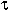 is a type defined in a header file created by
g2++comp(1C++),
then this is a typed
inserter or extractor.
A G2++ application uses typed inserters and extractors when
it has advance knowledge of record types.
The user must first compile definitions
of all such records using
g2++comp(1C++),
thereby
creating the header file(s) containing C++ type
definitions and their related operator
declarations.
The operator definitions are generated
in the corresponding .c files.
Typed inserters
and extractors do the work of the G2 functions getrec(),
getbody(), and putrec(), (functions that constitute
what Weythman calls G2's ``compiled interface''.
The behavior of the typed inserters
and extractors is specified in
typed_io(3C++).
is a type defined in a header file created by
g2++comp(1C++),
then this is a typed
inserter or extractor.
A G2++ application uses typed inserters and extractors when
it has advance knowledge of record types.
The user must first compile definitions
of all such records using
g2++comp(1C++),
thereby
creating the header file(s) containing C++ type
definitions and their related operator
declarations.
The operator definitions are generated
in the corresponding .c files.
Typed inserters
and extractors do the work of the G2 functions getrec(),
getbody(), and putrec(), (functions that constitute
what Weythman calls G2's ``compiled interface''.
The behavior of the typed inserters
and extractors is specified in
typed_io(3C++).
The function
g2seek() searches a stream for a G2++ record and returns the
name of the record.
The function comes in two overloaded versions:
g2seek(cin)
Scan the input stream for the next record and return its name.
g2seek(cin,"usr")
Scan the input stream for the next ``usr'' record
Following a call to g2seek(), the client is free to extract
the record or ignore it entirely.
The operator used to extract the record may be
typed or untyped, depending on how the client wishes to treat the record.
g2seek() is similar to the G2 function getname().
g2seek() is declared in g2++.h
and specified along with the untyped inserters
and extractors in
untyped_io(3C++).
Let us continue with the example.
After a typed extraction, each member of
the structure u will contain a value obtained from the input
record (or the appropriate null value if the
corresponding field was missing from
the record).
The client program can manipulate a given member using operations
applicable to objects of the member's type.
For example, an integer member can be
incremented.
After an untyped extraction, the nodes of the structure b
will be populated with the ASCII field names
and values from the input record, and
can be navigated by the client program.
There is currently no provision in
untyped_io(3C++)
for altering the structure of a
syntax tree; trees may only be navigated by following
root, child and
next pointers.
For example, suppose that the standard input contains a person
record followed by a usr record.
Tabs are used for indentation and also to separate field names from their
corresponding values.
person
name Bob
age 11
hobbies
0 swimming
1 tennis
usr
login jrd
id
usr 129
grp 159
name J.R. Dobbs
logdir /usr/bob
shell /usr/tools/bin/ksh
The first pass through the loop will result in an untyped extraction, creating
the following value in b:
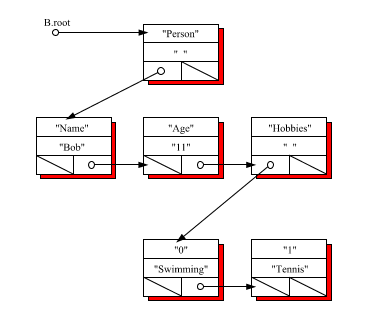
The second pass through the loop will result in a typed extraction, creating
the following value of u:
-
u.login will contain the string "jrd",
-
u.id.usr will contain the (long integer) value 129,
-
u.id.grp will contain the (short integer) value 159,
-
u.name will contain the string "J.R. Dobbs"
-
the u.proj array will contain four zeroes (there
was no project data in the record)
Note that the unexpected fields logdir and shell
were simply ignored.
Having just seen two functionally equivalent programs, don't conclude that
G2++ is mere syntactic ``sugar coating'' on G2.
The differences between G2 and
G2++ are quite significant,
as we hope to show in the remainder of this tutorial.
Next topic:
Support for iostream(3C++)
Previous topic:
Introduction to G2++
© 2004 The SCO Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
UnixWare 7 Release 7.1.4 - 27 April 2004
 , where
, where 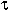 is a type defined in a header file created by
g2++comp(1C++),
then this is a typed
inserter or extractor.
A G2++ application uses typed inserters and extractors when
it has advance knowledge of record types.
The user must first compile definitions
of all such records using
g2++comp(1C++),
thereby
creating the header file(s) containing C++ type
definitions and their related operator
declarations.
The operator definitions are generated
in the corresponding .c files.
Typed inserters
and extractors do the work of the G2 functions getrec(),
getbody(), and putrec(), (functions that constitute
what Weythman calls G2's ``compiled interface''.
The behavior of the typed inserters
and extractors is specified in
typed_io(3C++).
is a type defined in a header file created by
g2++comp(1C++),
then this is a typed
inserter or extractor.
A G2++ application uses typed inserters and extractors when
it has advance knowledge of record types.
The user must first compile definitions
of all such records using
g2++comp(1C++),
thereby
creating the header file(s) containing C++ type
definitions and their related operator
declarations.
The operator definitions are generated
in the corresponding .c files.
Typed inserters
and extractors do the work of the G2 functions getrec(),
getbody(), and putrec(), (functions that constitute
what Weythman calls G2's ``compiled interface''.
The behavior of the typed inserters
and extractors is specified in
typed_io(3C++).
