|
|
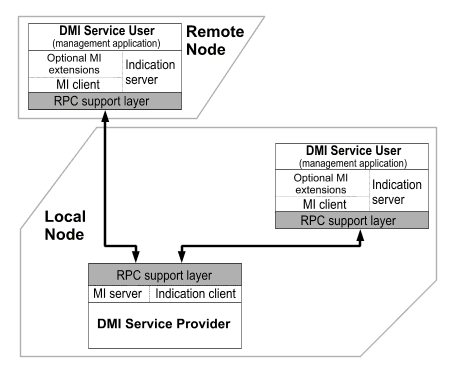
DMI 2.0 allows the Service Provider's functionality to be used by remoteable management applications. To enable the use of Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) as the DMI's remoting agent, the DMI specification includes a procedural API. Managing the DMI remotely is accomplished by a management application by first establishing a connection to that remote system, then registering with the remoteable DMI-SP in that system.
The DMI 2.0 Service Provider communicates with remote management applications through a procedural Management Interface. This procedural MI includes an RPC support layer between the DMI entities to hide the complexity of coordinating management functions across a network.
RPC is based on a client/server architecture. Communications between a ``DMI Service Provider'' (such as the DMI-SP) and a DMI ``service user'' (such as a management application) happen as client-server interactions coordinated by ``RPC support layers'' on either side.

Remoteable interface architecture
For performing management functions over the component MIF data, the DMI-SP supplies the ``Management Interface server'' (MI Server) and the management application supplies the ``Management Interface client'' (MI Client). For DMI implementations that support indications, the DMI-SP supplies the ``Indication client'', and the management application supplies the ``Indication server''.